深度学习模型,特别是用于图像分类的卷积神经网络(CNN),通常被看作是黑箱。我们知道它们能做出准确的预测,但很难直观地了解它们是根据图像的哪些部分来做出决策的。Grad-CAM(梯度加权类激活映射)是一种技术,它可以生成一张热力图,高亮显示出模型在进行特定预测时,图像中最重要的区域。这为我们提供了一种理解和解释模型行为的方法。
最初是因为自己的论文返修,编辑要求增加可解释性分析,最近做的差不多了,所以今天我根据一个实际的代码示例,撰写本文来介绍Grad-CAM的基本原理,并说明如何一步步实现它,以及在此过程中需要注意的一些实际问题。
什么是Grad-CAM
Grad-CAM的核心思想是利用梯度信息来理解卷积对于决策的重要性。它会检测模型最终输出的类别分数相对于某个卷积层特征图的梯度。这个梯度可以被看作是“为了增加这个类别的分数,特征图中每个像素点需要做出多大改变”的度量。
通过将这些梯度进行全局平均池化,可以得到每个特征图通道的“重要性权重”。然后,用这些权重去加权求和原始的特征图,再经过一个ReLU激活函数(只保留正值),就得到了一个粗糙的热力图。这张图显示了模型为了做出某个特定类别的预测,重点关注了图像中的哪些区域。
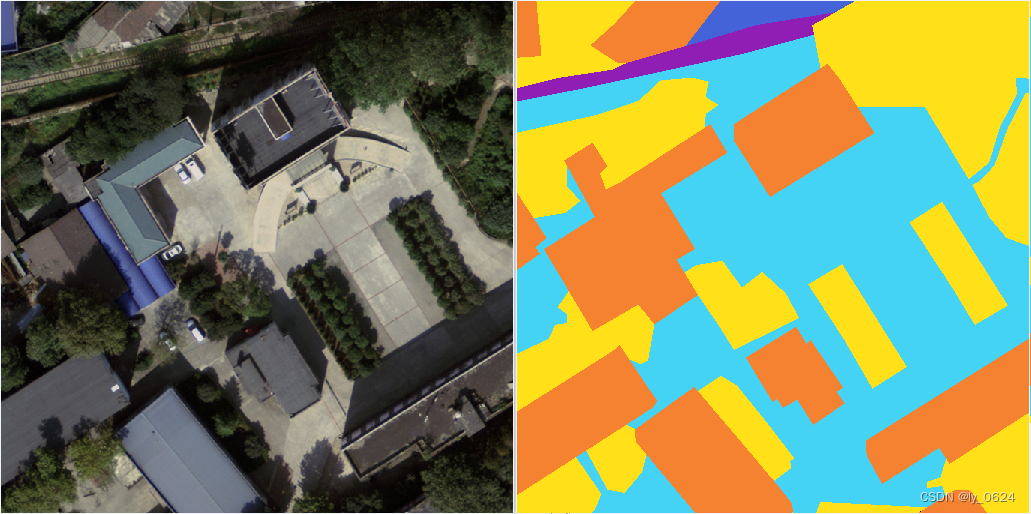
直观的看比如下方这张图:
![图片[1] - AI科研 编程 读书笔记 - 【人工智能】【Python】可解释性分析怎么做?使用Grad-CAM - AI科研 编程 读书笔记 - 小竹の笔记本](https://img.smallbamboo.cn/i/2025/11/18/691c791f7cc04.jpg)
这张图是一个基于CNN的模型在做作物病害分类任务。图中颜色越接近红色的地方代表模型越关注这个地方,可以看到图中玉米叶片的条形病斑被模型关注的比较多。
如何使用Grad-CAM分析自己的模型
在生成可解释性分析图片(热力图)之前,我们需要一个训练好的模型和一个想要分析的输入图像。实现Grad-CAM的主要步骤如下:
第一步是选择目标层。Grad-CAM需要作用于模型中的一个卷积层。理论上,任何卷积层都可以,但通常选择最后一个卷积层。因为这一层包含了最丰富的空间和语义信息,最能代表模型在分类前“看到”了什么。稍后提供的代码中的get_target_layer函数就是用来自动完成这个选择的。它会根据模型类的名称(如MobileNet、ResNet、Vision Transformer)来自动确定最后一个合适的层。当然如果你的模型最后的卷积层名称不同,可以自己手动指定。
第二步是生成热力图。代码中的apply_gradcam函数使用了pytorch-grad-cam这个第三方库来简化操作。先是用模型和上一步确定的目标层来初始化一个GradCAM对象。然后,确定一个目标类别。你可以手动指定一个类别索引,也可以让代码自动选择模型预测概率最高的那个类别。接着,将预处理后的图像张量和目标类别输入到GradCAM对象中,它就会计算并返回一个灰度热力图。这个热力图是一个二维数组,数值越大的地方代表模型对该区域的关注度越高。
第三步是可视化叠加,如果你直接输出刚刚生成的灰度图,可视效果并不好。科研论文中的普遍操作是将灰度图加一个透明度和彩色映射叠加到原始输入的彩色图片上,这样才能最终输出本文上面展示的图片的样子。代码中的visualize_cam_on_image函数先将灰度热力图(数值范围通常是0到1)转换为彩色的热力图,一般使用从蓝到红的色谱,红色代表高关注度。然后,将这张彩色热力图以一定的透明度与原始的RGB图像进行混合。最终生成的图像既保留了原始图像的内容,又通过颜色高亮了模型的关注区域。
下面我贴上自己使用的代码供大家参考,
import os
import time
import torch
import argparse
from torchvision import transforms
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from model import mobilenetv3_large as create_model
from my_dataset import MyDataSet
from utils import read_data, evaluate
from pytorch_grad_cam import GradCAM
from pytorch_grad_cam.utils.model_targets import ClassifierOutputTarget
from pytorch_grad_cam.utils.image import show_cam_on_image
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import cv2
def get_target_layer(model, model_type='auto'):
"""
自动检测或手动指定目标层
Args:
model: PyTorch 模型
model_type: 模型类型 ('auto', 'resnet', 'efficientnet', 'mobilenet',
'mobilenext', 'vit', 'swin', 'convnext', 'shiftingnet')
Returns:
target_layer: 用于 Grad-CAM 的目标层
"""
if model_type == 'auto':
# 自动检测模型类型
model_name = model.__class__.__name__.lower()
if 'resnet' in model_name:
return model.layer4[-1]
elif 'efficientnet' in model_name:
return model.features[-1]
elif 'mobilenet' in model_name:
return model.features[-1]
elif 'mobilenext' in model_name:
return model.features[-1] if hasattr(model, 'features') else model.blocks[-1]
elif 'vit' in model_name or 'vision' in model_name:
return model.blocks[-1].norm1
elif 'swin' in model_name:
return model.layers[-1].blocks[-1].norm1
elif 'convnext' in model_name:
return model.stages[-1]
elif 'shifting' in model_name:
return model.blocks[-1]
else:
# 尝试常见属性
if hasattr(model, 'blocks'):
return model.blocks[-1]
elif hasattr(model, 'features'):
return model.features[-1]
elif hasattr(model, 'layer4'):
return model.layer4[-1]
else:
raise ValueError(f"Cannot auto-detect target layer for {model_name}. "
f"Please specify model_type manually.")
# 手动指定
elif model_type == 'resnet':
return model.layer4[-1]
elif model_type == 'efficientnet':
return model.features[-1]
elif model_type == 'mobilenet':
return model.features[-1]
elif model_type == 'mobilenext':
return model.features[-1] if hasattr(model, 'features') else model.blocks[-1]
elif model_type == 'vit':
return model.blocks[-1].norm1
elif model_type == 'swin':
return model.layers[-1].blocks[-1].norm1
elif model_type == 'convnext':
return model.stages[-1]
elif model_type == 'shiftingnet':
return model.blocks[-1]
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unknown model_type: {model_type}")
def apply_gradcam(model, device, image_tensor, target_layer, class_idx=None):
"""应用 Grad-CAM 生成热力图"""
cam = GradCAM(model=model, target_layers=[target_layer])
if image_tensor.dim() == 3:
image_tensor = image_tensor.unsqueeze(0).to(device)
else:
image_tensor = image_tensor.to(device)
if class_idx is None:
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(image_tensor)
class_idx = int(outputs.argmax(dim=1).item())
print(f"Auto-detected target class: {class_idx}")
targets = [ClassifierOutputTarget(class_idx)]
grayscale_cam = cam(input_tensor=image_tensor, targets=targets)[0]
return grayscale_cam
def visualize_cam_on_image(rgb_img, heatmap, alpha=0.4):
"""将热力图叠加到原图上"""
heatmap = np.clip(heatmap, 0, 1)
# 手动生成热力图颜色映射
heatmap_uint8 = np.uint8(255 * heatmap)
heatmap_colored = cv2.applyColorMap(heatmap_uint8, cv2.COLORMAP_JET)
heatmap_colored = cv2.cvtColor(heatmap_colored, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
heatmap_colored = np.float32(heatmap_colored) / 255.0
# 叠加原图和热力图
overlay = heatmap_colored * alpha + rgb_img * (1 - alpha)
overlay = np.clip(overlay, 0, 1)
return overlay
def find_best_model(args, device, num_classes, test_loader, dataset_size):
"""遍历所有权重文件,找到测试准确率最高的模型"""
print("=" * 60)
print("Stage 1: Evaluating all model weights to find the best")
print("=" * 60)
model = create_model(num_classes=num_classes).to(device)
model.eval()
best_acc = 0.0
best_file = None
best_idx = None
total_round_time = 0.0
valid_rounds = 0
for idx in range(args.start_idx, args.end_idx + 1):
weight_file = os.path.join(args.weights_dir, f"model-{idx}.pth")
if not os.path.exists(weight_file):
print(f"Skipping missing file: {weight_file}")
continue
# 加载权重
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(weight_file, map_location=device))
print(f"\nEvaluating {weight_file}")
# 测量推理时间
if device.type.startswith('cuda'):
torch.cuda.synchronize()
start_time = time.perf_counter()
# 评估
test_loss, test_acc = evaluate(model=model,
data_loader=test_loader,
device=device,
num_classes=num_classes)
if device.type.startswith('cuda'):
torch.cuda.synchronize()
round_time = time.perf_counter() - start_time
print(f"Test Loss: {test_loss:.4f}, Test Accuracy: {test_acc:.4f}")
print(f"Round inference time: {round_time:.3f} seconds")
# 累计统计
total_round_time += round_time
valid_rounds += 1
# 更新最佳模型
if test_acc > best_acc:
best_acc = test_acc
best_file = weight_file
best_idx = idx
# 输出统计结果
if valid_rounds > 0:
avg_round_time = total_round_time / valid_rounds
avg_per_image = total_round_time / (valid_rounds * dataset_size)
print(f"\n--- Timing Summary ({valid_rounds} rounds) ---")
print(f"Average time per round: {avg_round_time:.3f} seconds")
print(f"Average time per image: {avg_per_image*1000:.3f} ms")
else:
print("No valid model files found in the specified range.")
return None, None, None
# 输出最优模型
if best_file:
print(f"\n{'='*60}")
print(f"Best model found: {best_file}")
print(f"Best Test Accuracy: {best_acc:.4f}")
print(f"{'='*60}\n")
return best_file, best_acc, best_idx
def gradcam_analysis(args, device, num_classes, best_weights_path, best_acc):
"""对最佳模型进行 Grad-CAM 可解释性分析"""
print("=" * 60)
print("Stage 2: Grad-CAM explainability analysis on best model")
print("=" * 60)
# 读取数据集
_, _, _, _, _, test_images_path, test_images_label = read_data(args.data_path)
# 图像预处理
img_size = {"s": 384, "m": 480, "l": 480}
num_model = "s"
data_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(img_size[num_model]),
transforms.CenterCrop(img_size[num_model]),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.5]*3, [0.5]*3)
])
# 创建模型并加载最佳权重
model = create_model(num_classes=num_classes).to(device)
state_dict = torch.load(best_weights_path, map_location=device)
model.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=False)
model.eval()
print(f"Loaded best weights: {best_weights_path}")
# 提取权重文件夹名称
weights_folder_name = os.path.basename(args.weights_dir)
# 对指定范围的图像进行 Grad-CAM 分析
os.makedirs(args.output_dir, exist_ok=True)
for img_idx in args.image_indices:
if img_idx >= len(test_images_path):
print(f"Warning: image index {img_idx} out of range, skipping")
continue
test_img_path = test_images_path[img_idx]
true_label = test_images_label[img_idx]
print(f"\nVisualizing image {img_idx}: {test_img_path}")
# 加载图像
img = Image.open(test_img_path).convert("RGB")
input_tensor = data_transform(img).to(device)
# 预测类别
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(input_tensor.unsqueeze(0))
pred_idx = torch.argmax(output, dim=1).item()
print(f"Predicted class: {pred_idx}, True label: {true_label}")
# 生成 Grad-CAM
target_layer = get_target_layer(model, model_type=args.model_type)
heatmap = apply_gradcam(model, device, input_tensor, target_layer, class_idx=None)
# 可视化叠加
rgb_img = np.array(img.resize((img_size[num_model], img_size[num_model]))).astype(np.float32) / 255.0
overlay = visualize_cam_on_image(rgb_img, heatmap, alpha=0.4)
result = (overlay * 255).astype(np.uint8)
# 保存结果(文件名包含权重文件夹名和准确率)
acc_str = f"{best_acc:.4f}".replace('.', '_')
save_name = f"gradcam_{weights_folder_name}_acc{acc_str}_img{img_idx}.jpg"
save_path = os.path.join(args.output_dir, save_name)
Image.fromarray(result).save(save_path)
print(f"Grad-CAM saved to: {save_path}")
print(f"\n{'='*60}")
print(f"Grad-CAM analysis completed for {len(args.image_indices)} images")
print(f"{'='*60}")
def main(args):
# 设置设备
device = torch.device(args.device if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(f"Using device: {device}\n")
# 读取数据集信息
num_classes, _, _, _, _, test_images_path, test_images_label = read_data(args.data_path)
print(f"Detected {num_classes} classes from dataset.")
print(f"Total test images: {len(test_images_path)}\n")
# 准备测试数据加载器
img_size = {"s": 384, "m": 480, "l": 480}
num_model = "s"
data_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(img_size[num_model]),
transforms.CenterCrop(img_size[num_model]),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.5]*3, [0.5]*3)
])
test_dataset = MyDataSet(images_path=test_images_path,
images_class=test_images_label,
transform=data_transform)
batch_size = args.batch_size
num_workers = min(os.cpu_count(), batch_size if batch_size > 1 else 0, 8)
print(f"Using {num_workers} dataloader workers")
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=False,
pin_memory=True,
num_workers=num_workers,
collate_fn=test_dataset.collate_fn)
# Stage 1: 找到最佳模型
best_weights_path, best_acc, best_idx = find_best_model(
args, device, num_classes, test_loader, len(test_dataset)
)
if best_weights_path is None:
print("No valid weights found. Exiting.")
return
# Stage 2: 对最佳模型进行 Grad-CAM 分析
gradcam_analysis(args, device, num_classes, best_weights_path, best_acc)
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
description="Find best model by test accuracy and perform Grad-CAM analysis"
)
# 数据和设备相关
parser.add_argument('--data-path', type=str, default="new_datasets/MixCorn",
help='Path to dataset root')
parser.add_argument('--device', default='cuda:0',
help='Device (e.g., cuda:0 or cpu)')
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=32,
help='Batch size for DataLoader')
# 权重文件相关
parser.add_argument('--weights-dir', type=str, required=True,
help='Directory containing model-*.pth files')
parser.add_argument('--start-idx', type=int, default=80,
help='Start index of model files')
parser.add_argument('--end-idx', type=int, default=99,
help='End index of model files')
# Grad-CAM 相关
parser.add_argument('--image-indices', type=int, nargs='+', default=[0, 1, 2],
help='Indices of test images to visualize (space-separated)')
parser.add_argument('--output-dir', type=str, default='gradcam_results',
help='Directory to save Grad-CAM results')
parser.add_argument('--model-type', type=str, default='auto',
choices=['auto', 'resnet', 'efficientnet', 'mobilenet',
'mobilenext', 'vit', 'swin', 'convnext', 'shiftingnet'],
help='Model architecture type for target layer selection')
args = parser.parse_args()
main(args)
'''
使用示例:
# 自动检测模型类型(推荐)
python one_times_gradcam.py \
--data-path ../ShiftingNet/datasets/MixCorn \
--weights-dir weights_ablation_CFS_ablation/MC_DC_2025_11_11_08_54_59 \
--start-idx 80 --end-idx 99 \
--batch-size 32 --device cuda:0
# 手动指定模型类型
python one_times_gradcam.py \
--data-path ../ShiftingNet/datasets/MixCorn \
--weights-dir weights_efficientnet/EfficientNetB0_2025_07_10 \
--start-idx 80 --end-idx 99 \
--model-type efficientnet \
--batch-size 32 --device cuda:0
# 指定多张图像进行可视化
python one_times_gradcam.py \
--data-path ../datasets/MixCorn \
--weights-dir weights/MC2025_04_26_13_17_22 \
--start-idx 80 --end-idx 99 \
--image-indices 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800\
--output-dir my_gradcam_output \
--batch-size 32 --device cuda:0
'''一些些注意事项
图像预处理要和模型训练时要保持一致。代码中定义了一个data_transform,包含了缩放、中心裁剪、转换为张量以及归一化等操作。在进行Grad-CAM分析时,输入的图像必须经过完全相同的预处理流程,否则模型可能无法正确识别图像,导致生成的热力图没有意义。
然后目标层的选择很重要。虽然通常选择最后一个卷积层,但对于一些特殊的模型结构,比如ViT,可能没有传统意义上的卷积层。在这种情况下,需要选择一个合适的替代层,例如最后一个Transformer块中的某个模块。
值得大家了解的是,Grad-CAM并不是万能的。它提供的是一种关于模型决策依据的直观参考,但它本身也是一种近似。有时,它可能会高亮一些看似不相关的背景区域,或者无法精确地圈出目标的完整轮廓。因此,在分析结果时,应将其作为一种辅助诊断工具,而不是绝对的真相。将多张图像的 Grad-CAM 结果结合起来进行分析,一般来说能得到更可靠的结论。
本文就写到这里,希望对你有所帮助。
2. 论文总结类文章中涉及的图表、数据等素材,版权归原出版商及论文作者所有,仅为学术交流目的引用;若相关权利人认为存在侵权,请联系本网站删除,联系方式:i@smallbamboo.cn。
3. 违反上述声明者,将依法追究其相关法律责任。
























暂无评论内容