#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int fib(int n){
if (n<2){
return n;
}
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2);
}
int main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
cout << fib(n);
return 0;
}
数据量大时,不适宜使用递归,而是使用动态规划(备忘录)。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
vector<int> dp;
int f(int n){
if (dp[n]){ // 记忆化递归
return dp[n];
}
if (n<2){
return dp[n] = n;
}
return dp[n] = f(n-1) + f(n-2);
}
int fib(int n){
dp.resize(n+1, 0); // 重新定义dp大小,初始化为0
return f(n);
}
int main(){
int times;
cin >> times;
while (times--){
int n;
cin >> n;
cout << fib(n) << endl;
}
return 0;
}© 版权声明
1. 除特殊说明外,本网站所有原创文章的版权归作者所有,未经授权,禁止以任何形式(包括但不限于转载、摘编、复制、镜像等)发布至任何平台。
2. 论文总结类文章中涉及的图表、数据等素材,版权归原出版商及论文作者所有,仅为学术交流目的引用;若相关权利人认为存在侵权,请联系本网站删除,联系方式:i@smallbamboo.cn。
3. 违反上述声明者,将依法追究其相关法律责任。
2. 论文总结类文章中涉及的图表、数据等素材,版权归原出版商及论文作者所有,仅为学术交流目的引用;若相关权利人认为存在侵权,请联系本网站删除,联系方式:i@smallbamboo.cn。
3. 违反上述声明者,将依法追究其相关法律责任。
THE END


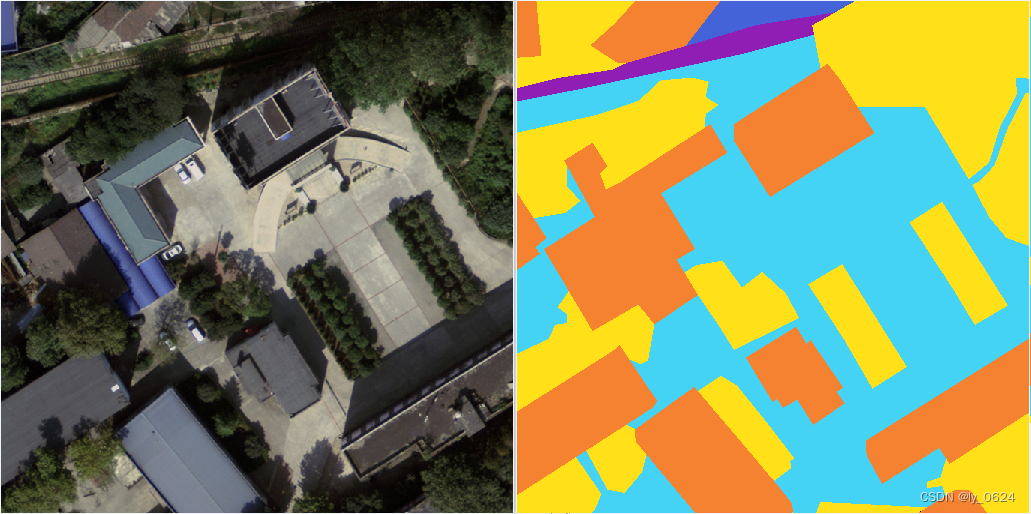


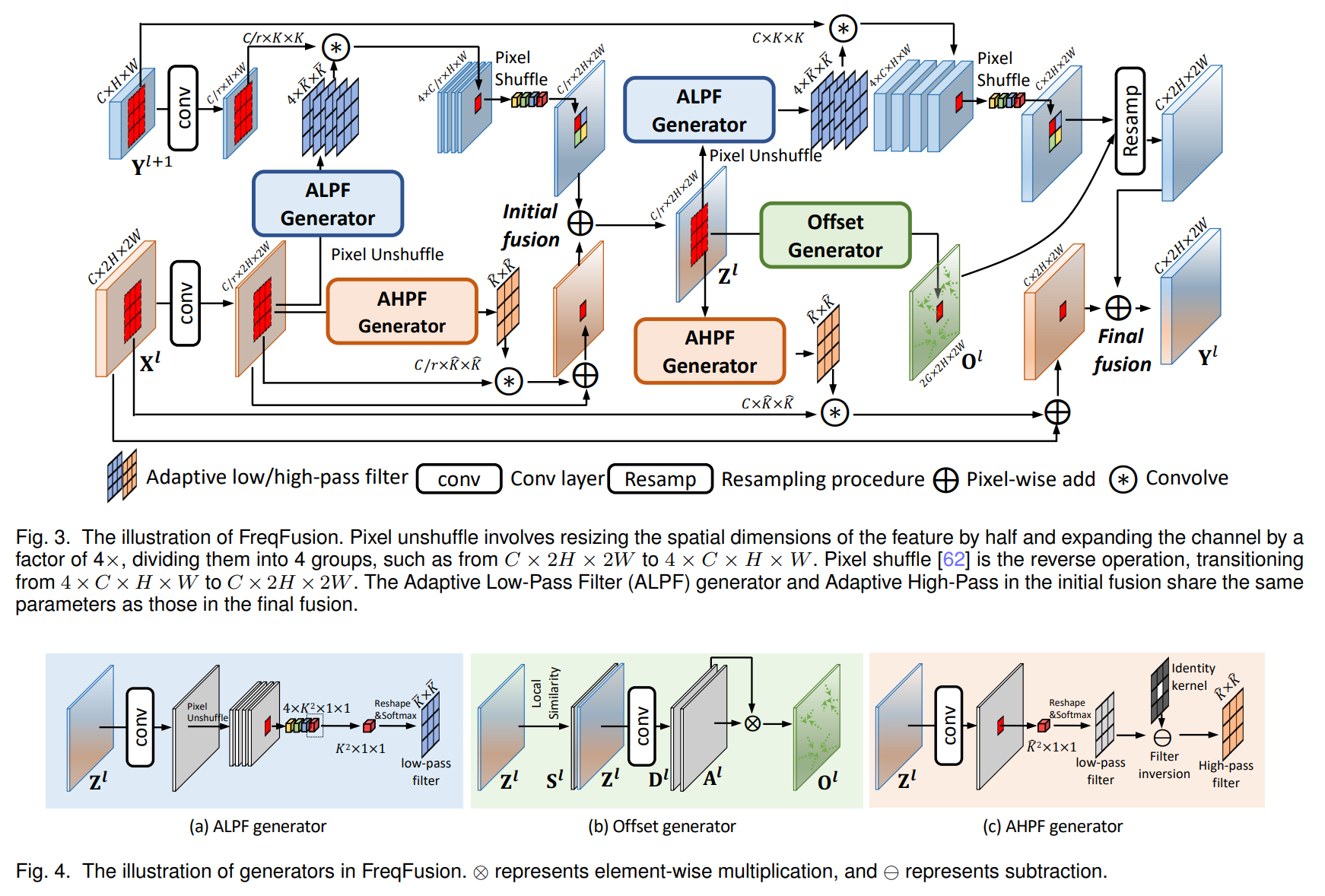
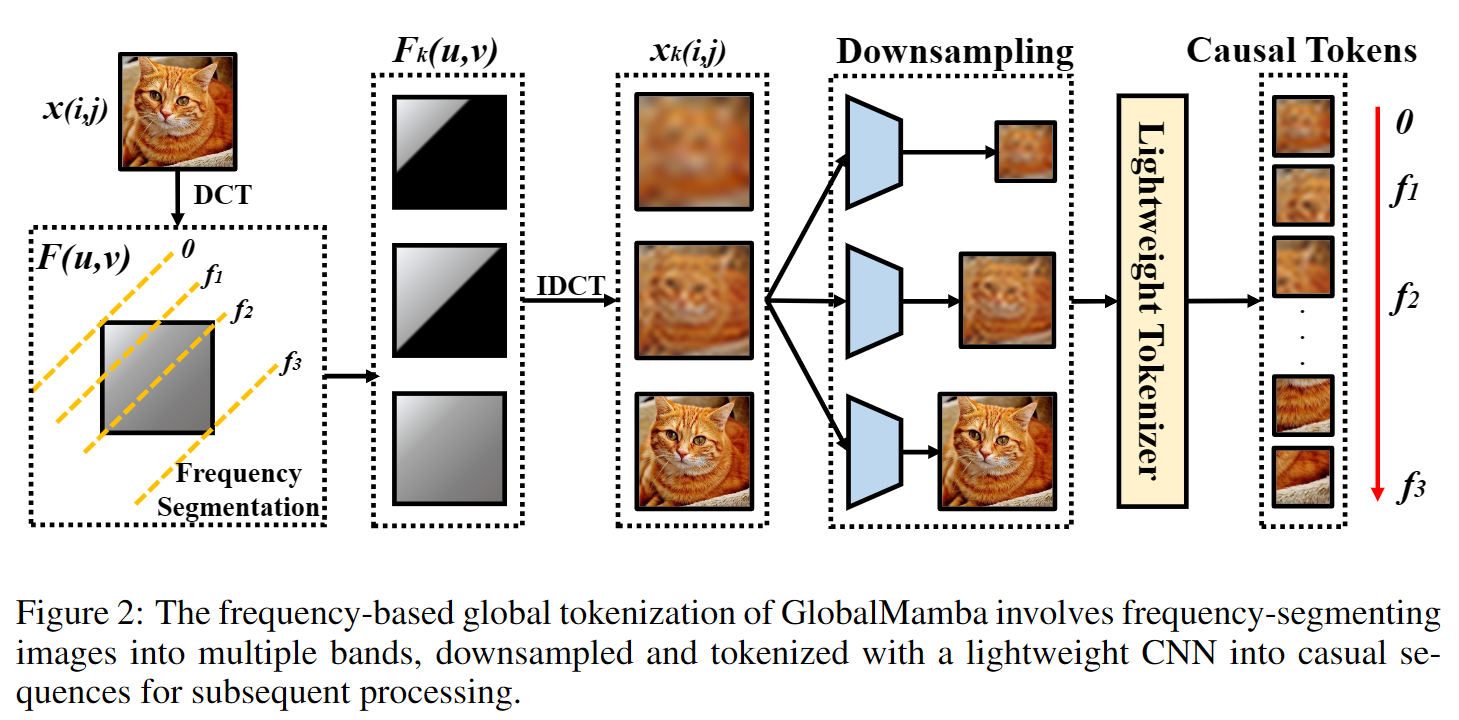

















暂无评论内容